
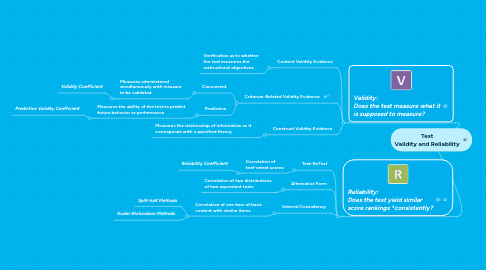
how consistent or dependable (which refers to reliability), and.Social researchers primarily employ two criteria for evaluating the quality of their measures. Situational errors are ones that occur neither at random nor systematically but occur as a result of particular personal characteristics of the individual(s) or other special circumstances that can influence the measurement process.įatigue, for example, of the respondents or an unusual environmental detraction, may generate a situational error. Likewise, a defective weighing machine or any other defective measuring device is likely to produce a systematic error in the measuring process. In the measurement of contraceptive use, for example, if people consistently report higher use, because they believe the interviewer or the program managers would appreciate this, errors would take place systematically, giving a false high rate of contraceptive use. Unlike random error, the sum of the systematic errors does not add to zero. Incorrect operationalization of variables.Faulty conceptualization of the research problem.Systematic errors frequently occur as a result of improper research procedures such as Observations, which consistently overestimate or underestimate the true value, are subject to systematic error.

The inaccuracy of measurements that repeatedly occurs and for the same reasons is labeled systematic error. While reporting, some people will overstate their age, and some will understate. Sometimes people do not know their exact age. If the errors are truly random, they will cancel each other, and the overall average of these errors will be zero.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
